Introduction
Large language models are becoming increasingly capable of handling complex, multi-step tasks. Advances in reasoning, multimodality, and tool use have unlocked a new category of LLM-powered systems known as agents.
This guide is designed for product and engineering teams exploring how to build their first agents, distilling insights from numerous customer deployments into practical and actionable best practices.
What are you looking to learn?
Take this quick quiz to help us direct you to the most relevant sections:
What is your current level of familiarity with AI agents?
What aspect of agents are you most interested in?
Guide Overview
What is an Agent?
Understand the fundamental concepts of AI agents and how they differ from conventional software.
Learn MoreWhen to Build an Agent?
Discover the scenarios where agents can add the most value to your workflows and processes.
Learn MoreAgent Design Foundations
Explore the key components and architecture of effective agent systems.
Learn MoreGuardrails
Learn how to implement safety measures and ensure your agents operate reliably.
Learn MoreAgent Architecture
At its most fundamental form, an agent consists of three key components working together:
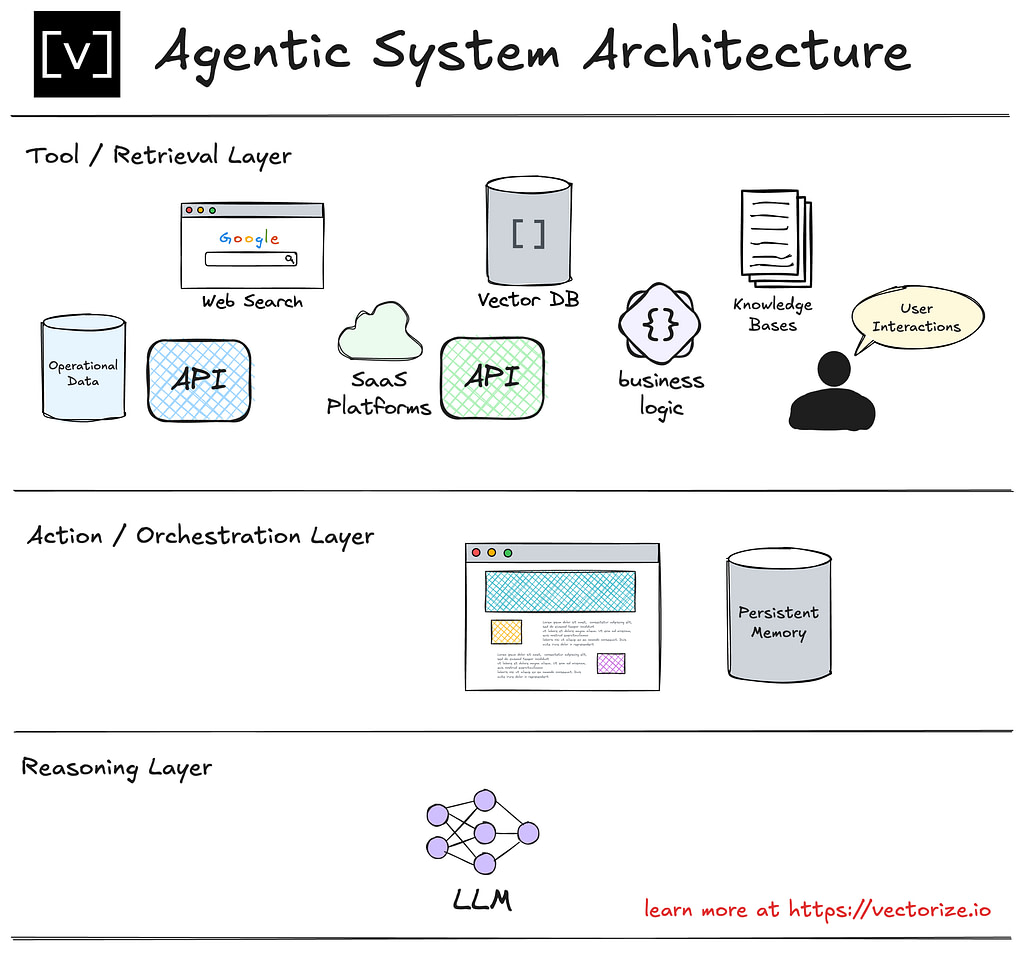
The foundation of the system. This layer interfaces with external data sources and services, including APIs, vector databases, operational data, knowledge bases, and user interactions. It's responsible for fetching the raw information the system relies on.
This layer is responsible for brokering the interactions between the LLM and the outside world (the tools). It handles interactions with the user, when applicable. It receives instructions from the LLM about which action to take next, performs that action, then provides the result to the LLM in the reasoning layer.
The core of the system's intelligence. This layer processes the retrieved information using a large language model (LLM). It determines what the agent needs to do next, leveraging context, logic, and predefined goals.
Track Your Progress
Complete all sections to master the fundamentals of building AI agents!